In the era of data-driven innovation, access to information has become essential for any organization seeking to lead in their field. However, with the rise in data access, there is also an urgent need for transparent, ethical, and secure data usage to protect individual privacy and sensitive business information. This is where the European Union’s new Data Governance Act (DGA), formally known as Regulation (EU) 2022/868, introduces a new regulatory landscape designed to address these complexities.
The Data Governance Act (DGA) represents a crucial framework designed to facilitate data sharing across the EU while safeguarding sensitive information. It aims to establish a trusted environment where data can be reused safely, paving the way for a data economy that benefits individuals, organizations, and society.
Understanding the DGA: trust and structure for data sharing
The DGA aims to promote data sharing while safeguarding sensitive information. To achieve this, it introduces measures that address several critical aspects:
Regulation of protected data reuse: The DGA introduces guidelines for the reuse of certain types of publicly held data, such as personal information or commercially sensitive data. This means that organizations can only reuse protected data if it is anonymized or aggregated to prevent re-identification. This regulation ensures that data reuse complies with privacy standards while still allowing organizations to leverage valuable information, especially in fields like healthcare and scientific research, where the reuse of sensitive data can lead to critical innovations.
Data intermediation services: The DGA also regulates data intermediation services, which act as brokers between data holders and data users, ensuring these transactions meet privacy standards. By setting standards for these intermediaries, the DGA enhances trust in data-sharing activities, helping organizations confidently engage in data transactions that meet regulatory demands. Data intermediaries also help streamline data access for organizations, reducing the complexity and risks often associated with cross-border data exchanges.
Data altruism: The Act promotes data sharing for altruistic purposes, this aspect allows individuals and organizations to voluntarily contribute their data for projects with a social benefit, such as research in public health or environmental sustainability, without a profit motive. By creating a legal structure for data altruism, the DGA promotes a more inclusive and socially responsible data ecosystem, empowering organizations to support public-interest initiatives and participate in impactful research.
European Data Innovation Board: To oversee the DGA's implementation, the Act establishes a European Data Innovation Board, which is responsible for setting best practices, defining standards, and promoting cross-sectoral collaboration across the EU. This board will help harmonize data-sharing efforts across different industries, ensuring that organizations adhere to uniform standards and benefit from the shared knowledge of best practices. It will also provide guidance on resolving potential conflicts between the DGA and other regulations, such as the GDPR.
New challenges and compliance needs for data-driven sectors
For organizations that heavily rely on data, the DGA presents both a structural shift and a compliance challenge. The Act’s requirements for anonymization and controlled data access demand sophisticated technical solutions, and the need to use secure data processing environments requires organizations to reassess their data-handling protocols.
Some common challenges include:
Anonymization and Aggregation:Organizations must develop strategies to ensure that data is properly anonymized or aggregated to prevent re-identification, which can be technically demanding and resource-intensive.
Adherence to privacy standards:The DGA requires compliance with the GDPR and ePrivacy regulations, ensuring that if a conflict arises between the DGA and these laws, GDPR and ePrivacy take precedence.
Exclusivity limits: To prevent monopolization, the DGA limits exclusive data-sharing arrangements to one year in special cases, forcing companies to adapt to new ways of accessing data through non-exclusive channels.
Dedomena’s solutions: enabling compliant and effective data use
In this current regulatory climate, ensuring data privacy and compliance has become a central challenge for data-driven organizations. Regulations like the GDPR in Europe and the CCPA in the United States have established strict rules for handling personal data, creating restrictions for organizations that depend on data to drive AI and machine learning initiatives. For these organizations, Dedomena AI offers innovative solutions centered on synthetic data, enabling safe and compliant data usage while maximizing the value of data assets.
Data Anonymization: Dedomena AI provides sophisticated tools for anonymizing data, ensuring compliance with the DGA’s requirements for secure reuse of sensitive information. These processes help organizations meet regulatory standards without compromising data utility.
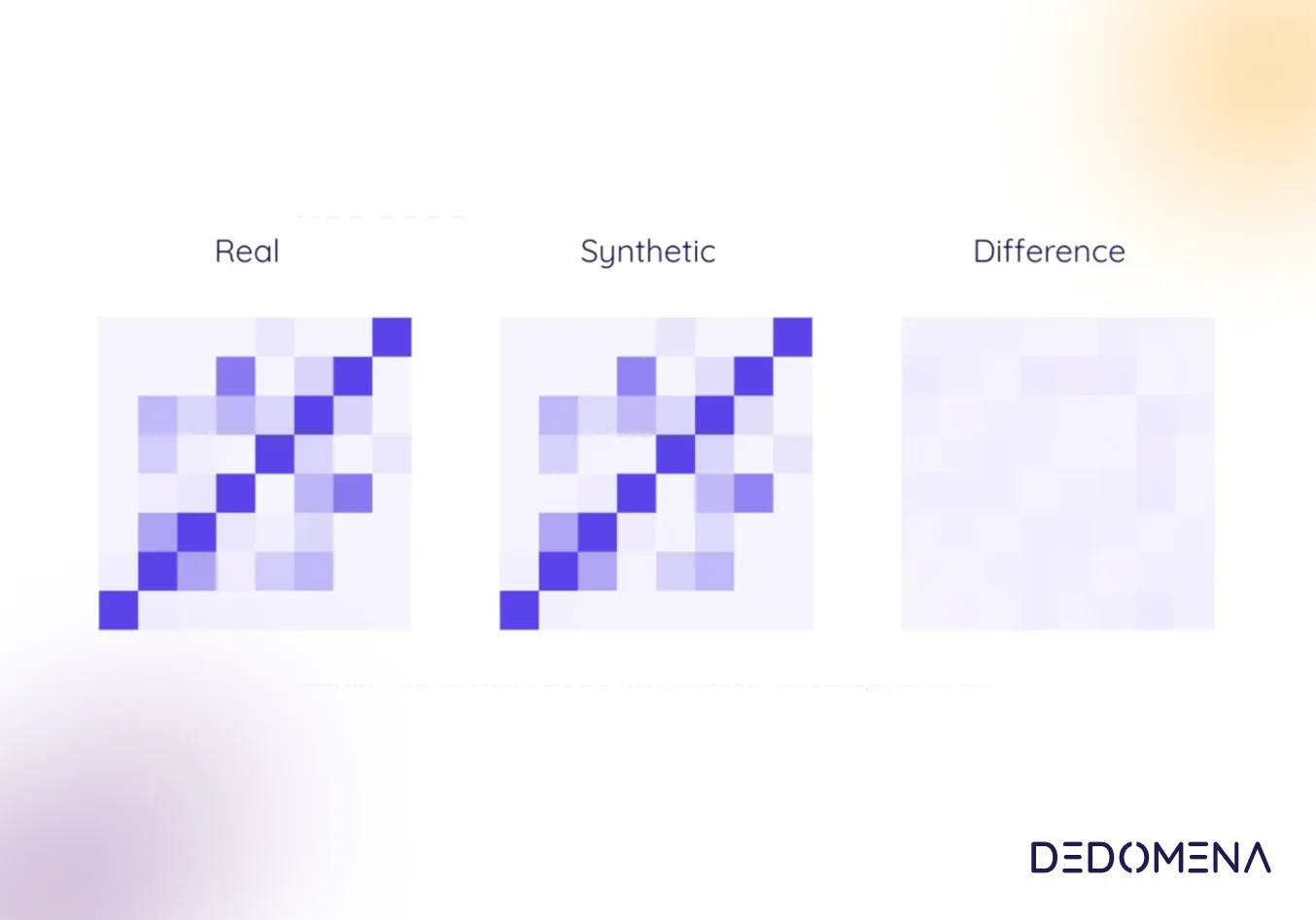
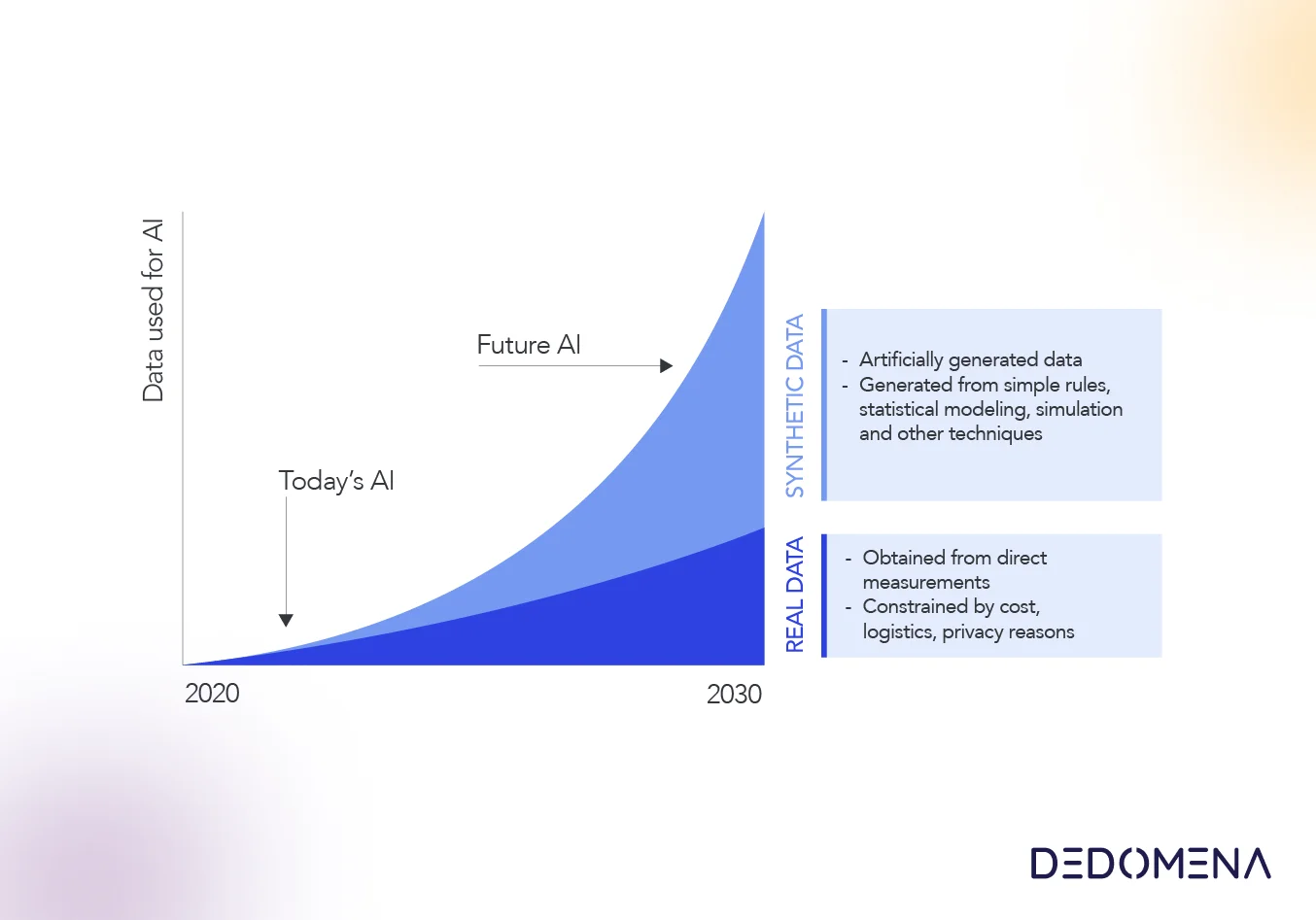
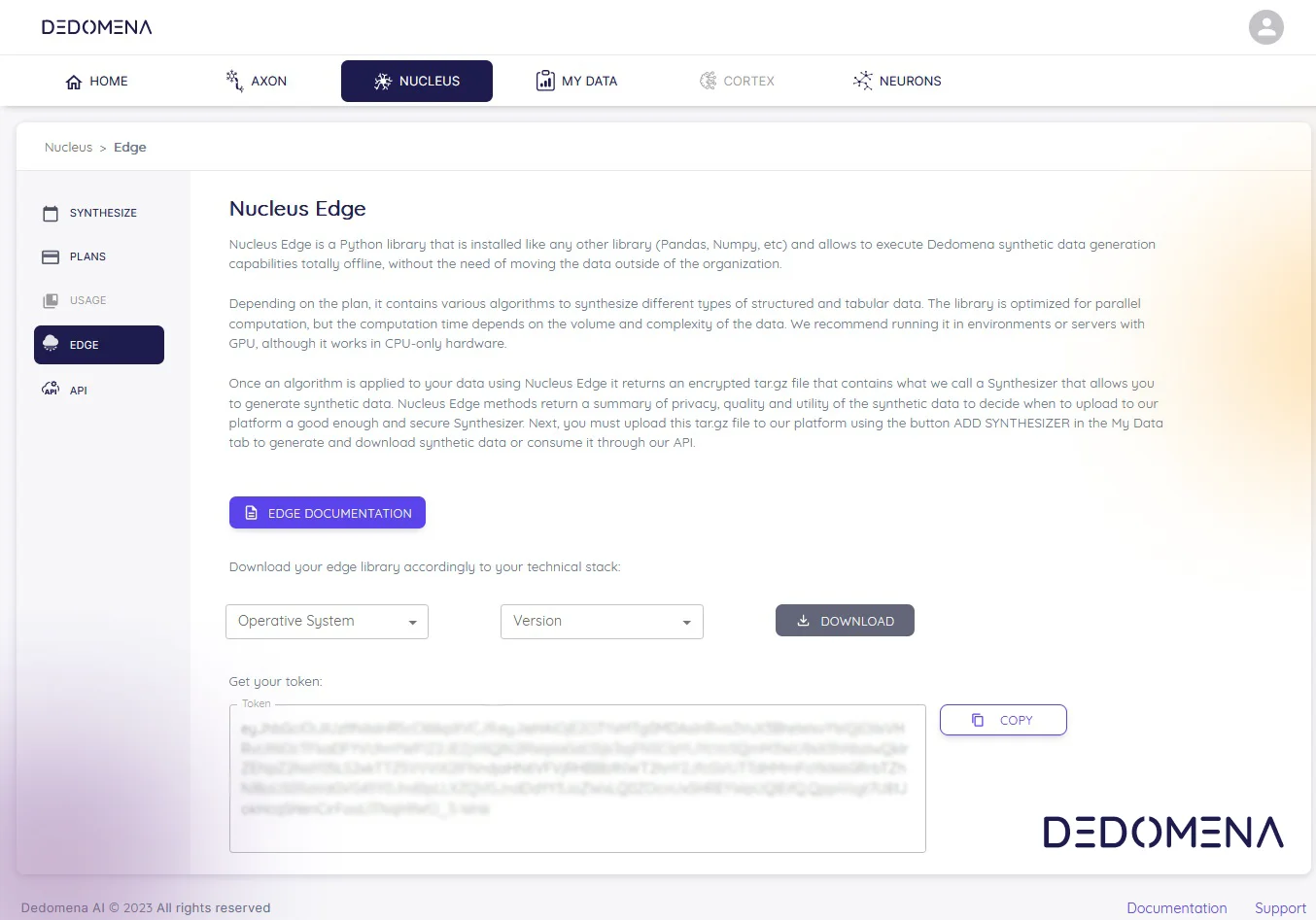
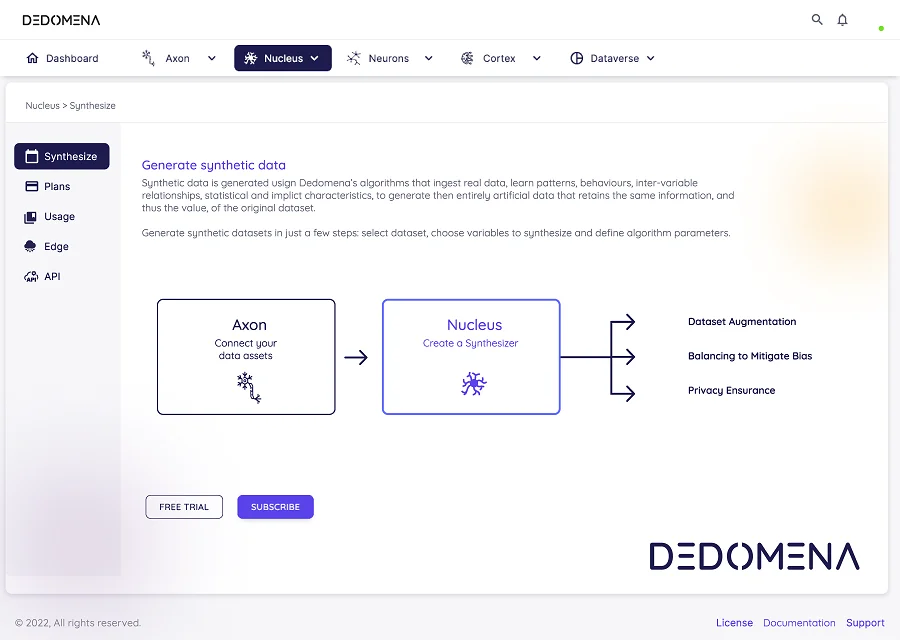
One of Dedomena’s most powerful compliance tools is its synthetic data software. Synthetic data is generated artificially while maintaining the statistical properties of the original data. This means it can be used to train machine learning models, validate AI applications, and conduct exploratory data analysis without the risk of exposing real customer information. By replacing real data with synthetic counterparts, Dedomena enables organizations to comply with the strictest privacy restrictions, as synthetic data is 100% anonymous, secure and does not require additional customer consent for secondary uses, thus aligning seamlessly with privacy-focused regulations.
Secure data processing environments: To meet DGA requirements for data security, Dedomena offers secure processing environments or sandboxes that allow for controlled access to data, enabling organizations to analyze and use sensitive information without risking unauthorized re-identification. These environments have been designed to align with EU standards for data protection, providing organizations with peace of mind in their data-sharing activities.
Data compliance and governance solutions: Dedomena’s platform integrates data governance features that help organizations manage, track, and document data usage in alignment with DGA requirements.
The Data Governance Act is a milestone for data-driven sectors, offering a framework that promotes innovation while ensuring privacy and security. As organizations strive to adapt to these new rules, Dedomena AI stands ready to provide the solutions necessary for compliant, secure, and effective data use.
By leveraging Dedomena’s platform, organizations can unlock the value of their data assets, drive insights, and achieve strategic goals in a responsible and legally compliant manner.
Our synthetic data solution not only helps organizations meet regulatory demands but also provides significant flexibility. Without the constraints of personal data compliance, data-driven projects can be executed with speed and precision, free from the time-intensive requirements for anonymization, consent, or other privacy processes typically mandated by data protection laws.
As we continue to support our clients in navigating this new era of data regulation, we encourage data-driven organizations to explore Dedomena’s comprehensive suite of compliance and governance solutions.
For more insights on compliant data use, check out our previous blog post on the transformative power of synthetic data in regulated sectors.
Which data protection methods do you need for privacy?
References
Implementing the Data Governance Act – guidance document, European Comission, Last update, 24 September 2024.