Overcoming challenges in the Health industry
The healthcare industry is undoubtedly one of the most complex and sensitive sectors when it comes to data access and processing.
The main reason why health data access and processing is so important is due to the extreme delicacy of the information that makes up this data, since it contains elements such as illness that individuals suffers or have suffered, the consequences thereof, the types of tests they have undergone, or the medicines that were administered to them.
For this reason, incorporating synthetic data generation along the process of accessing and processing healthcare data is considered a key element when it comes to help data scientists to create solutions capable of detecting and predicting diseases, or even collaborating in obtaining new cures and treatments for those diseases
Data challenges in the Healthcare industry
As we have seen in previous articles, the application of data-driven decisions involves a number of challenges when it comes to accessing private and sensitive data. Within the healthcare sector specifically, there are two main challenges that must be addressed::
1. Privacy and data regulations
Probably no sector demands more privacy than the health sector. The information that medical centres and companies deal with encompases extrimely intimate details about individuals' health situation. There are a number of data privacy regulations that impact the the health industry, including:
-
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR):
In Europe, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets out the guidelines for the collection, storage, use and protection of patient information. It applies to all organizations that work in healthcare areas and require access to a certain amount of personal data for using it solely for specific health activities.
-
The digital Care Act (DVG):
This German regulation outlines that digital health applications must comply with data protection and security requirements. Also, the key element is allowing doctors to prescribe digital health apps, which are then backed by insurance companies.
-
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA):
This rule establishes a series of national standards that ensure that medical information is protected. HIPAA also sets a checklist for healthcare service providers to follow in order to protect healthcare-related information. such as the transmission, access, integrity, and auditing of the data.
2. Healthcare data comes from different sources
A wide range of sources contribute to this sector's data collection, including hospital records, medical records, examinations, and wearable devices. Having such a variety of sources, the format in which the data are presented can vary, as some provide structured data, whereas others may present unstructured data (for example, images), as each source will have its own type of information.
Interpreting and collecting healthcare data from various sources is a very important part of developing and maintaining patient care. By gaining a broad and deep understanding of specific health conditions, doctors will be able to treat them effectively. It takes a lot of time and effort to complete and purge this type of data, even with the patient's explicit consent. However, complying with all data security and privacy requirements will not guarantee that data scientists are working with quality data and enough of it for building new disease prevention and prediction models.
3. Health data is unstructured
There is an estimated 80% of data that is unstructured within healthcare organizations, so it's important to be aware of what is available and not to accidentally share sensitive data. Organizations should have processes and technology in place to identify, extract, structure and anonymize this sensitive information in whatever systems, messages and documents in which it exists.
New AI and machine learning techniques are able to identify code words by understanding not only what's in a document, image or message, but also the context around it, including the clinical structure of the patients involved.
By using AI to automate the process of accessing patient data, healthcare organizations can save both time and money, while understanding customers' data and avoiding issues like potential data breaches.
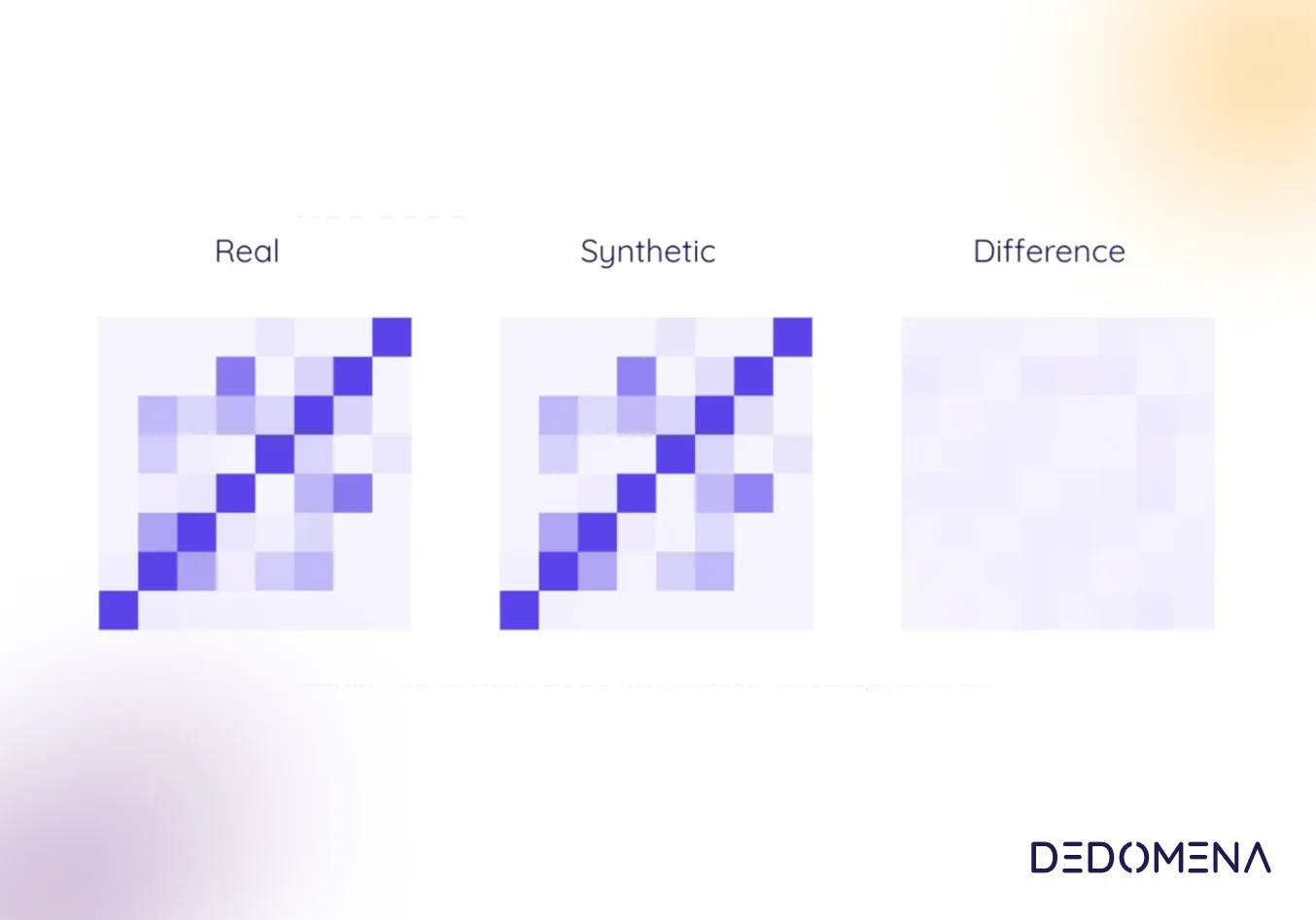
In recent years, synthetic data has received considerable attention as a method of protecting patient privacy and augmenting clinical research. Synthetic data carries the ability to create fake patient records and fake medical imaging that is truly non-identifiable because the data does not relate to any real individual. The potential benefits and applications of using synthetic data as a driver for innovation in the healthcare industry is huge, and now companies are starting to realise it.