The rise of data-driven innovation has transformed many industries and created new business opportunities, allowing companies to gain valuable insights into customer behaviour, market trends, and operational efficiency. However, with the growing concern over data privacy and security, governments around the world have started to implement regulations to protect individuals´data rights. One such regulation is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which was introduced by the European Union in 2018. In this blog post, we will explore the impact of data privacy regulations like GDPR on the future of innovation, looking into the impact it has on business and individuals, as well as how synthetic data can help overcome the challenges of accessing sensitive and private data under this type of regulations.
The GDPR is a comprehensive data privacy regulation that sets out rules on how organizations can collect, process, and store personal data. It applies to any organization that collects or processes data of EU citizens, regardless of where the organization is based. The GDPR provides individuals with more control over their personal data and requires organizations to obtain explicit consent from individuals before collecting and processing their data. The regulation also imposes significant penalties for non-compliance, including fines of up to €20 million or 4% of a company's global annual revenue.
The Impact of GDPR on Businesses
While the GDPR has been a welcome change for individuals´data privacy rights, it has also had a significant impact on businesses. One of the biggest challenges is the increased regulatory burden for organizations that need to comply with GDPR´s strict requirements. Companies that collect and process personal data need to ensure that they are compliant with GDPR, which means implementing new processes, technologies and procedures, such as obtaining consent, managing data breaches, and responding to data subject requests. This has led to increased costs and slowed down the innovation process for the majority of companies.
For instance, many businesses have had to invest in new technology and personnel to ensure compliance with such regulations. Larger companies may have been able to absorb the costs of GDPR compliance, but smaller companies may have found it more challenging to do so. As a result, some companies have struggled to innovate as quickly as they would like, leading to a competitive disadvantage compared to businesses that are not affected by GDPR.
However, the GDPR has also created opportunities for innovation in the data privacy industry. Companies that specialize in providing GDPR compliance solutions, such as data privacy management and synthetic data generation software, have seen increased demand for their products and services. This has led to the emergence of new startups and niche companies that focus solely on data privacy and compliance.
In addition, the GDPR has also helped to create a culture of data privacy awareness among individuals and organizations. Consumers are now more aware of their data privacy rights and are more likely to demand transparency from companies on how their data is being collected and processed. This has led to more innovation in privacy-enhancing technologies, such as blockchain-based systems that allow individuals to track and control their data, or synthetic data generation technology that allows companies to use personal data securely and effectively. As a result, businesses that are able to implement effective data privacy solutions can differentiate themselves from their competitors by offering their customers greater data privacy protection.
The Impact of GDPR on Individuals
The GDPR has had a significant impact on individuals´data privacy rights. The regulation gives individuals greater control over their personal data, including the right to access, rectify, and delete their data at any time. It also requires organizations to obtain explicit consent from individuals before collecting and processing their data. This means that individuals have more control over their data and are more aware of how it is being used.
As a result of the GDPR, individuals are more likely to demand transparency from companies on how their data is being collected and processed. This has led to a shift in the way that companies think about data privacy. Rather than viewing data privacy as a compliance issue, many companies now view it as an opportunity to build trust with their customers. Companies that are able to demonstrate that they are taking data privacy seriously are more likely to earn the trust and loyalty of their customers. In turn, this can lead to a competitive advantage and increased business success. Therefore, businesses that prioritize data privacy and transparency not only comply with the GDPR but also benefit from a positive reputation and customer base.
Using Synthetic Data for Innovating in the Data Protection era
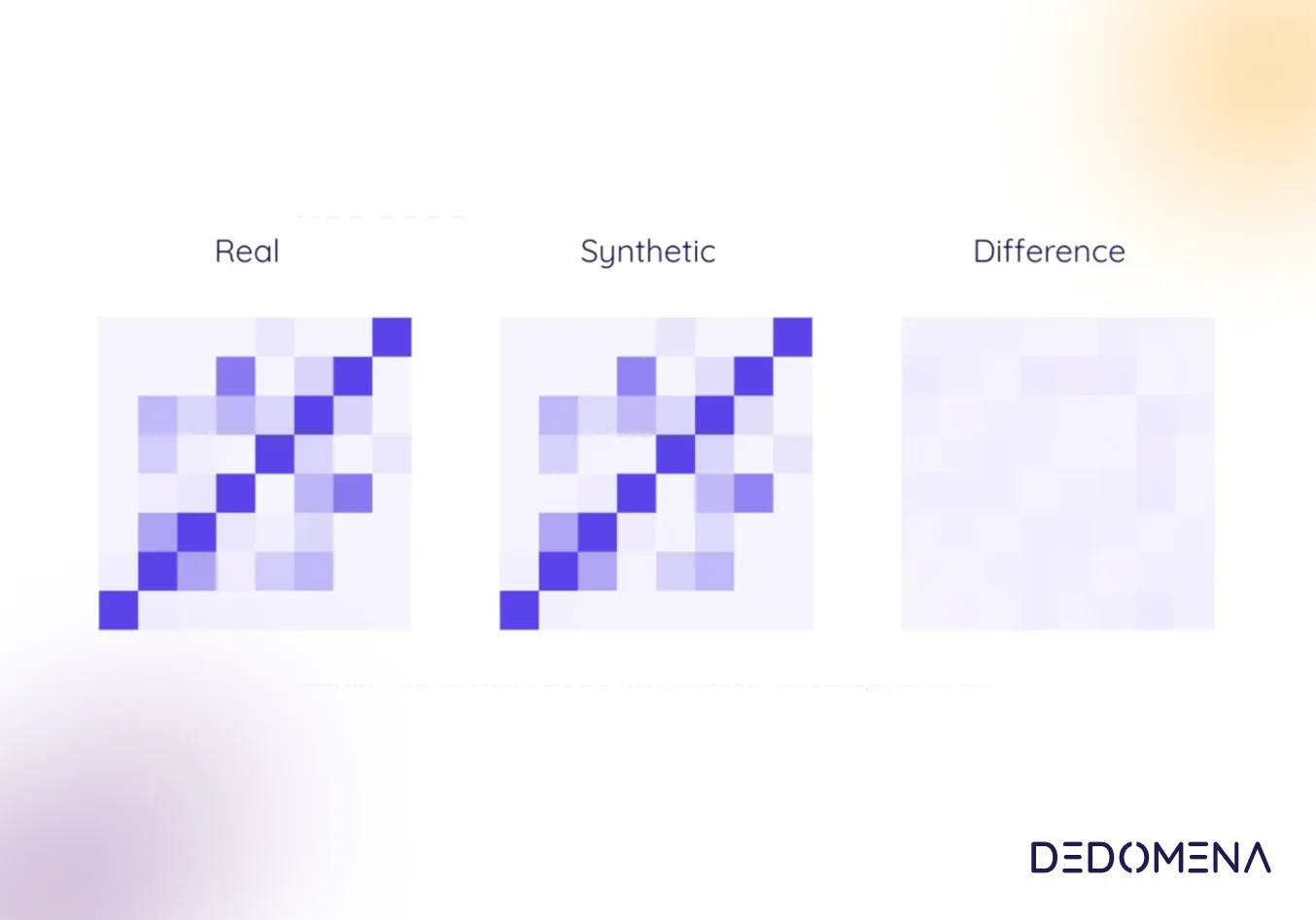
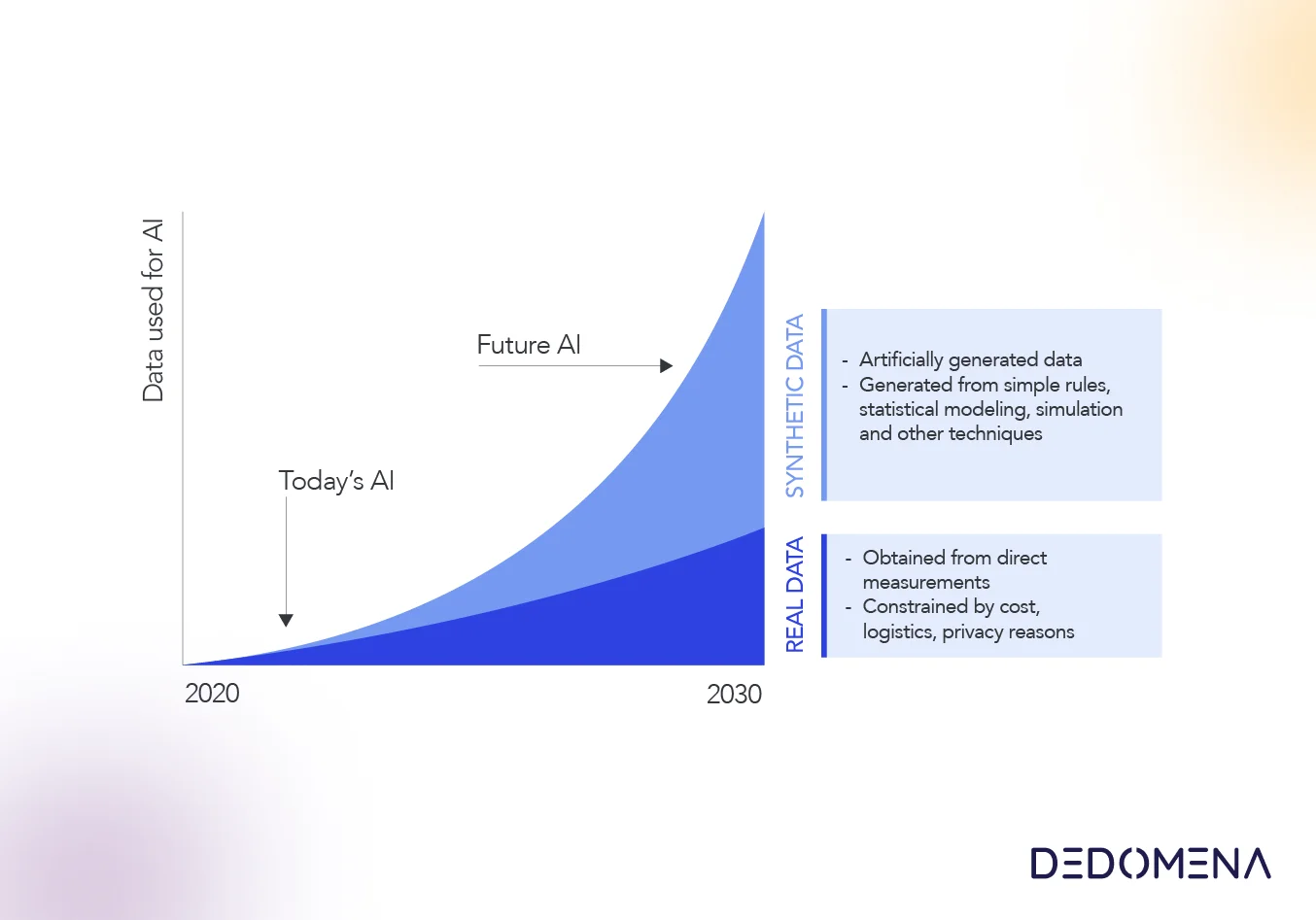
One solution for innovating in the current data protection environment is the use of synthetic data. Synthetic data is artificially generated data that resembles real data but does not contain personally identifiable information. This data can be used to train artificial intelligence models, to share data within departments and companies, and to harness the full potential of personal data without violating individuals' privacy.
Synthetic data is generated using data generation techniques such as neural network generation and generative adversarial algorithms. These methods allow the creation of large amounts of synthetic data that resembles real data but do not contain any personally identifiable information. The use of synthetic data allows companies to innovate while complying with data protection laws such as the GDPR. For example, a bank could use synthetic data to train a machine learning model that can predict financial behaviours and the effectiveness of a cross-selling campaign. The bank can use these synthetic data to train models without having to worry about individuals´privacy. In this way, the company can innovate while ensuring compliance with data protection laws.
In addition, the use of synthetic data can also improve the quality of artificial intelligence models. As synthetic data is artificially generated, the characteristics of the data can be controlled, which can improve the accuracy and quality of the model by, for instance, reducing bias or performing data augmentation. This can help companies improve operational efficiency and decision-making.
In summary, the use of synthetic data is a promising solution for innovating in the current data protection environment. These data allow companies to comply with data protection laws while innovating and improving the quality of their artificial intelligence model and boosting their data-driven strategy. As data protection laws continue to evolve, the use of synthetic data is likely to become a common practice in business innovation.